WATER
Water is an elixir of life that helps in transport of nutrients, excretion of waste and regulation of hormones.
It also controls the distribution of body salts & helps to control body temperature.
EDIBLE ANTIOXIDENTS
Antioxidants are scavengers of free radicals and their inclusion in diet is very important in daily life to prevent
chronic diseases and degeneration of cells.
- Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA &DHA): inhibits inflammation. e.g. fish (salmon, mackerel , tuna, sardines, herring, bluefish), shrimp, monosaturated oils (canola, flaxseed, olive oil)
- Vitamin A (beta-carotene): Inactivates free radicals. e.g. liver, fortified milk, egg, carrots, spinach, kale, apricots, papaya, mango, oatmeal, peas, peaches, red pumpkin.
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid): scavenge free radicals and inhibits inflammatory metabolites. e.g. red pepper, kiwi, orange, grapefruit, strawberries, papaya, broccoli, sweet potato, pineapple, kale, mango, tomato juice.
- Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol): e.g. fortified cereal, sunflower seeds, almonds, sunflower oil, hazelnuts, peanuts, peanut butter, peanut oil, safflower oil, olive oil, corn oil, canola oil, turnip greens, spinach, and avocado.
- Selenium: e.g. tuna, beef, cod, turkey, chicken, enriched noodles, egg, bread, oatmeal, rice, cottage cheese, walnuts
- Flavonoids: e.g. fruits & vegetables.
- Ubiquinone (CoQ10): e.g. meat, fish, poultry
A “5 W” plan of eating: what to eat? When to eat? Where to eat? Why to eat? Ways to eat? Is imminent in following and maintaining a healthy dietary schedule.
One should take a balanced diet at regular intervals, in stress free environment, to meet nutritional requirements to protect one from illness and chronic diseases.
A dramatic increase in the prevalence of overweight and obesity among all the age groups has occurred in last 2-3 decades. About 30-50% of adult Indians are either overweight or obese.
Overweight and obese individuals are at an enhanced risk of co-morbidities including type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, psycho- social problems. Hence dietary modification is important in timely prevention of these diseases.
DIETARY MODIFICATION IN OBESITY
- Achieve energy balance and appropriate weight for height with slow and steady reduction.
- Include fruits, vegetables and whole grains at each meal.
- Limit trans-fats (processed & refined foods)
- Avoid foods with increased amounts of sugar, salt.
- Avoid soft drinks and alcohol.
- Limit saturated fatty meats and substitute with lean meats and sea food.
- Replace whole milk dairy products with low fat or non –fat milks, cheese and yoghurts.
- Increase monounsaturated fats (nuts,seeds,avocados,olive and peanut oils)
- Severe fasting & feasting may lead to health hazard.
- Encourage regular physical activity.
- Eat meals regularly at frequent intervals.
- Fat soluble vitamins - Vit A, D, E, K
- Water soluble vitamins – Vit. B, & Cl
Sources: fruits, vegetables, whole grain cereals, nuts and oil seeds
MINERALS are required for building bones, regulating water balance, nerve and muscle control and energy production.
- Calcium- e.g. green leafy vegetables, milk, cheese, buttermilk, curd.
- Phosphorus - e.g. Cereals, pulses, nuts, oilseeds.
- Iron – e.g. Whole cereals, whole pulses, green leafy vegetables, Jaggery, pomegranate, egg.
- Zinc –e.g. nuts, pumpkinseeds, flaxseeds, spinach, seafood, brown rice.
DIETARY MODIFICATION IN HYPERTENSION
- Restrict the intake of added salt right from an early age.
- Develop a taste for foods/diet that is low in salt.
- Restrict intake of preserved and processed foods such as papads, pickles ,sauces ,ketchup, salted biscuits, chips,cheese and salted fish.
- Eat plenty of vegetables and fruits. They are good source of potassium.
- Use always iron fortified iodized salt (double fortified salt).
- Follow a DASH diet (Plenty of fruits,Vegetables,Wholegrains and Omega3 Fats)
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Reduce stress
- Maintain ideal body weight
- Include good fats
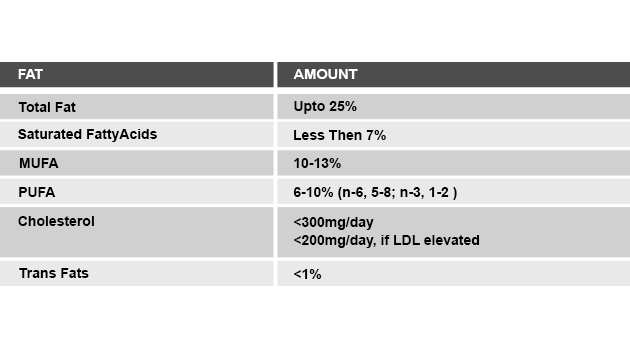
- Cut back on foods that are high in saturated fat, cholesterol, and trans fats.
DIETARY MODIFICATION IN CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
- Calories should be sufficient to maintain appropriate body weight for a given height.
- Physical activity for half an hour everyday can bring down the risk.
- Avoid alcohol
- Diet rich in fruits, vegetables and whole cereal grains.
- Avoid excess salt & sugar
- Limit use of processed and pre-prepared food items
- Minimum use of saturated fats & cholesterol
DIETARY MODIFICATION IN DIABETES
- Avoid simple sugars and sweet products.
- Eat meals at regular times & avoid fasting
- Small frequent meals
- Do not skip meals
- Watch your portion sizes
- Incorporate exercise in your routine
DIETARY MODIFICATION TO REDUCE STRESS
- Increase amount of anti-oxidants as provitamins A, C, E & Flavanoids
- Include protein-rich diet
- Include trace elements as zinc, selenium & copper
- Plenty of citrus fruits
- Reduce spices, chilies, coffee, sugars & soft drinks
- No to alcoholic beverages
- Include natural antibiotics
- Drink plenty of fluids
FINALLY, NATURES PRISCRIPTION FOR A HEALTHY LIVING WILL BE…
- EAT TO LIVE ,DO NOT LIVE TO EAT
Maintain a desirable body weight
- CLEAN UP THE OILY MESS
Reduce total fat and saturated fat. Avoid cholesterol and use vegetable oils in moderation.
- HE WHO FOLLLOWS NATURE IS NEVER OUT OF THE WA
Eat natural foods as grown, like coarse grains, whole grain cereals and pulses, and vegetables, avoid refined foods, processed foods and sugar.
- NATURE IS BOUNTIFUL,SO STAY CLOSE TO IT
Eat more fresh fruits and vegetables. If you like fish, eat 2-3 times a week.
- A LITTLE SALT IS DIVINE.BUt TOO MUCH IS HARMFUL
Cut down salt use, eat foods in natural state. Keep the salt intake low.
- THERE IS A DEVIL IN EVERY BERRY OF THE GRAPE.
Avoid alcohol
- DON’T GET REDUCED TO ASHES
Don’t smoke
- THE WISE DEPEND ON EXERCISE FOR FITNESS
Take to regular exercise
- HOPE FOR THE BEST AND DON’T DRIVE YOURSELF TO DEATH
Get to know the source of your stress and avoid it. relax!
Make a habit of living healthy....For yourself, your family & the society.
REFERENCES:
- Dietary guidelines for Indians, ICMR, 2011.
- Source: dietary guidelines for Indians, ICMR, 2011
- Source: Diet and diabetes, T.C.Raghuram, NIN, ICMR 2012r