How it works to help you lose weight?
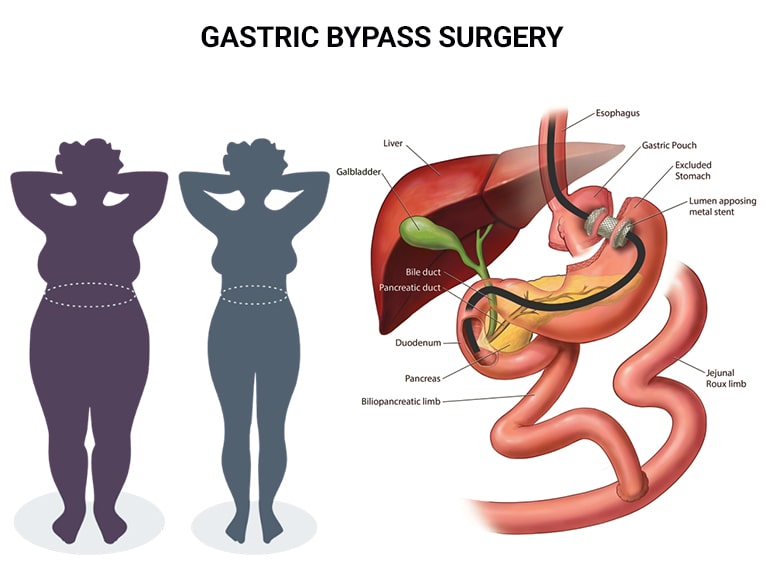
Gastric bypass, which combines restrictive and malabsorptive surgery techniques, is the most frequently performed bariatric procedure in the United States. In this procedure, stapling creates a small (15 to 20 cc) stomach pouch. The remainder of the stomach is not removed, but is completely stapled shut and divided from the lower stomach pouch. The outlet from this newly formed pouch empties directly into the lower portion of the jejunum, thus bypassing calorie absorption and the duodenum. To achieve this, the small intestine is divided just beyond the duodenum and a connection with the new, smaller stomach pouch is constructed. The length of either segment of the intestine can be increased to produce lower or higher levels of malabsorption.
Obesity becomes morbid obesity when an adult is 45 kgs or more over ideal body weight, has a BMI of 40 or more, or has a BMI of 35 or more in combination with a health-related condition such as obstructive sleep apnea or a disease such as type 2 diabetes or heart disease.